Serverless Cloud Portfolio
Architecture: A Blueprint for Resilient Design and Automated Lifecycle Management
Project Overview
This project is a full-stack, serverless application that serves as my professional cloud engineering portfolio. It demonstrates a complete transition from manual cloud configurations to a modern, event-driven architecture—managed entirely through Infrastructure as Code (IaC) and protected by a robust CI/CD pipeline.
Technical Architecture
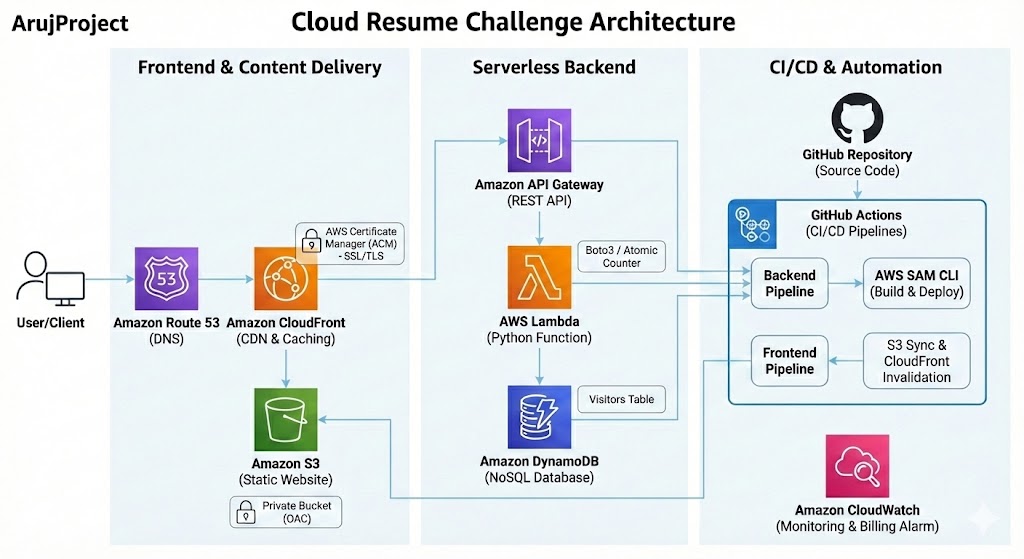
1. Global Frontend & Security
- Storage (Amazon S3): Static assets (`index.html`, `project.html`) are stored in an S3 bucket with Block Public Access enabled to prevent direct data exposure.
- Content Delivery (CloudFront): A global CDN serves the site via HTTPS. It utilizes Origin Access Control (OAC) to securely fetch content from the private S3 bucket, ensuring the bucket is never accessed directly by the public.
- DNS & Identity: Domain management is handled by Amazon Route 53 using A-Alias records. End-to-end encryption is enforced by an SSL/TLS certificate provisioned via AWS Certificate Manager (ACM).
2. Serverless Backend (Visitor Counter)
- API Layer (API Gateway): Exposes a RESTful endpoint that handles incoming requests from the frontend JavaScript.
- Compute (AWS Lambda): A Python function (using the `boto3` library) processes the visitor logic. It utilizes Atomic Updates to ensure count accuracy during high-traffic concurrency.
- Persistence (DynamoDB): A NoSQL database stores the visitor count in a single-item table, optimized for sub-millisecond response times.
3. Automation (The DevOps Lifecycle)
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): The entire backend—permissions, database schema, and API triggers—is defined in an AWS SAM (Serverless Application Model) template for total reproducibility.
-
CI/CD Pipelines (GitHub Actions):
- Backend: Automatically runs Python tests (using Moto to mock AWS services). On success, it builds and deploys the SAM stack to AWS.
- Frontend: Automatically synchronizes code changes to S3 and triggers a CloudFront Invalidation to clear the global cache, making updates visible instantly.
Project Specifications
| Category | Technology & Specification |
|---|---|
| Cloud Provider | Amazon Web Services (AWS) |
| Infrastructure | S3, CloudFront, Route 53, API Gateway, Lambda, DynamoDB |
| IaC Tooling | AWS SAM (Serverless Application Model) |
| Languages | Python (Backend), JavaScript (Frontend), YAML (IaC) |
| CI/CD Platform | GitHub Actions |
| Testing Framework | Pytest & Moto (Mocking library) |
Lessons Learned & Strategic Reflection
The CORS Hurdle: Mastering the "handshake" between the browser and the API Gateway was a critical learning curve. I had to ensure the Lambda function returned specific headers to allow the frontend to communicate securely across different domains.
Least Privilege & Zero Trust: Designing IAM roles that give the Lambda function only the permission it needs to talk to DynamoDB was a priority. This mirrors the "protocol-driven" precision required in medical diagnostics—where every action must be intentional, verified, and restricted to the necessary scope.
Manual vs. Automated: Moving from "clicking in the console" to defining infrastructure as code fundamentally changed my approach to building systems. The result is a highly available, professional portfolio that operates at a total cost of $0.00/month under the AWS Free Tier, proving that cloud-native solutions can be both powerful and cost-effective.